<when> syntax
Conditions allowed in the when portion of a rule must extend GraphOperation and currently include evaluation of Java classes, XML files, projects, and file content. Because XML rules are modeled after the Java-based rule add-ons, links to JavaDocs for the related Java classes are provided for a better understanding of how they behave.
The complete XML rule schema is located here: http://windup.jboss.org/schema/windup-jboss-ruleset.xsd.
The following sections describe the more common XML when rule conditions.
-
<javaclass> condition syntax
-
<xmlfile> condition syntax
-
<project> condition syntax
-
<filecontent> condition syntax
-
<file> condition syntax
-
<has-hint> condition syntax
-
<has-classification> condition syntax
-
<graph-query> condition syntax
-
<dependency> condition syntax
By default, if more than one when rule condition is provided, then all conditions must be met for the rule to match.
<javaclass> syntax
Summary
Use the <javaclass> element to find imports, methods, variable declarations, annotations, class implementations, and other items related to Java classes. For a better understanding of the <javaclass> condition, see the JavaDoc for the JavaClass class.
The following is an example of a rule that tests for WebLogic-specific Apache XML packages:
<rule id="weblogic-03000">
<when>
<javaclass references="weblogic.apache.xml.{*}" />
</when>
<perform>
<hint title="WebLogic Specific Apache XML Package" effort="1" category-id="mandatory">
<message>
Code using this package should be replaced with code using the org.apache.xml package from [Apache
Xerces](http://xerces.apache.org/).
</message>
</hint>
</perform>
</rule>Construct a <javaclass> element
<javaclass> element attributes
| Attribute name | Type | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
references |
CLASS_NAME |
The package or class name to match on. Wildcard characters can be used. This attribute is required.
references="weblogic.apache.xml.{*}"
|
||
matchesSource |
STRING |
An exact regex to match. This is useful to distinguish hard-coded strings. This attribute is required. matchesSource="log4j.logger" |
||
as |
VARIABLE_NAME |
A variable name assigned to the rule so that it can be used as a reference in later processing. See the as="MyEjbRule" |
||
from |
VARIABLE_NAME |
Begin the search query with the filtered result from a previous search identified by its from="MyEjbRule" |
||
in |
PATH_FILTER |
Filter input files matching this regex (regular expression) naming pattern. Wildcard characters can be used. in="{*}File1"
|
<javaclass> child elements
| Child Element | Description |
|---|---|
<location> |
The location where the reference was found in a Java class. Location can refer to annotations, field and variable declarations, imports, and methods. For the complete list of valid values, see the JavaDoc for TypeReferenceLocation. |
<annotation-literal> |
Match on literal values inside of annotations. The following example matches on Note that in this case, the |
<annotation-type> |
Match on a particular annotation type. You can supply subconditions to be matched against the annotation elements. The below example would match on a |
<annotation-list> |
Match on an item in an array within an annotation. If an array index is not specified, the condition will be matched if it applies to any item in the array. You can supply subconditions to be matched against this element. The below example would match on Note that in this case, the |
<xmlfile> syntax
Summary
Use the <xmlfile> element to find information in XML files. For a better understanding of the <xmlfile> condition, see the JavaDoc for the XmlFile class.
The following is an example of a rule that tests for an XML file:
<rule id="<UNIQUE_RULE_ID>">
<when>
<xmlfile matches="/w:web-app/w:resource-ref/w:res-auth[text() = 'Container']">
<namespace prefix="w" uri="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"/>
</xmlfile>
</when>
<perform>
<hint title="Title for Hint from XML">
<message>Container Auth</message>
</hint>
<xslt description="Example XSLT Conversion" extension="-converted-example.xml"
template="/exampleconversion.xsl"/>
</perform>
</rule>
Construct an <xmlfile> element
<xmlfile> element attributes
| Attribute name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
matches |
XPATH |
Match on an XML file condition. matches="/w:web-app/w:resource-ref/w:res-auth[text() = 'Container']" |
xpathResultMatch |
XPATH_RESULT_STRING |
Return results that match the given regex. <xmlfile matches="//foo/text()" xpathResultMatch="Text from foo."/> |
as |
VARIABLE_NAME |
A variable name assigned to the rule so that it can be used as a reference in later processing. See the as="MyEjbRule" |
in |
PATH_FILTER |
Used to filter input files matching this regex (regular expression) naming pattern. Wildcard characters can be used. in="{*}File1"
|
from |
VARIABLE_NAME |
Begin the search query with the filtered result from a previous search identified by its from="MyEjbRule" |
public-id |
PUBLIC_ID |
The DTD public-id regex. public-id="public" |
<xmlfile> matches custom functions
The matches attribute may use several built-in custom XPath functions,
which may have useful side effects, like setting the matched value on the rule variables stack.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
|
Match a XPath expression against a string, possibly containing {ProductShortName} parameterization placeholders. matches="windup:matches(//foo/@class, '{javaclassname}')"
This will match all |
<xmlfile> child elements
| Child element | Description |
|---|---|
<namespace> |
The namespace referenced in XML files. This element contains two optional attributes: The |
<project> syntax
Summary
Use the <project> element to query the Maven POM file for the project characteristics. For a better understanding of the <project> condition, see the JavaDoc for the Project class.
The following is an example of a rule that checks for a JUnit dependency version between 2.0.0.Final and 2.2.0.Final.
<rule id="UNIQUE_RULE_ID">
<when>
<project>
<artifact groupId="junit" artifactId="junit" fromVersion="2.0.0.Final" toVersion="2.2.0.Final"/>
</project>
</when>
<perform>
<lineitem message="The project uses junit with the version between 2.0.0.Final and 2.2.0.Final"/>
</perform>
</rule>Construct a <project> element
<project> element attributes
The <project> element is used to match against the project’s Maven POM file. You can use this condition to query for dependencies of the project. It does not have any attributes itself.
<project> child elements
| Child element | Description |
|---|---|
<artifact> |
Subcondition used within |
<artifact> element attributes
| Attribute name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
groupId |
PROJECT_GROUP_ID |
Match on the project |
artifactId |
PROJECT_ARTIFACT_ID |
Match on the project |
fromVersion |
FROM_VERSION |
Specify the lower version bound of the artifact. For example |
toVersion |
TO_VERSION |
Specify the upper version bound of the artifact. For example |
It is possible to qualify the element within the POM file that contains the artifact that the rule is searching for.
This is achieved using the optional <location> element.
The example below shows a rule that is searching for an artifact within the <plugins> element of the POM file.
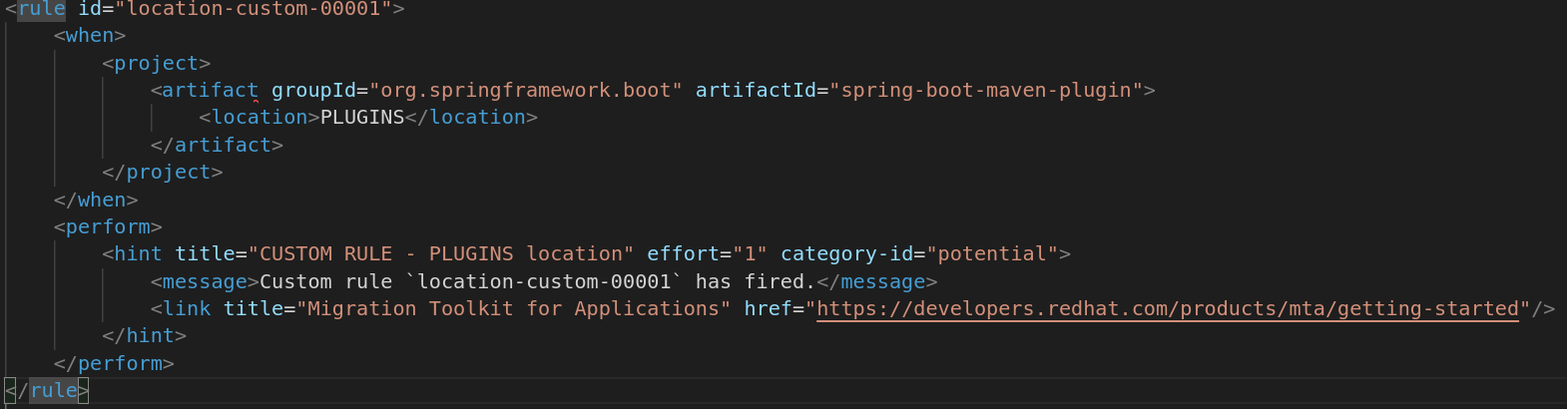
The valid list of locations is as follows:
-
DEPENDENCY_MANAGEMENT
-
DEPENDENCIES
-
PLUGIN_MANAGEMENT
-
PLUGINS
-
PARENT
<filecontent> syntax
Summary
Use the <filecontent> element to find strings or text within files, for example, a line in a Properties file. For a better understanding of the <filecontent> condition, see the JavaDoc for the FileContent class.
Construct a <filecontent> element
<filecontent> element attributes
| Attribute name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
pattern |
String |
Match the file contents against the provided parameterized string. This attribute is required. |
filename |
String |
Match the file names against the provided parameterized string. |
as |
VARIABLE_NAME |
A variable name assigned to the rule so that it can be used as a reference in later processing. See the as="MyEjbRule" |
from |
VARIABLE_NAME |
Begin the search query with the filtered result from a previous search identified by its from="MyEjbRule" |
<file> syntax
Summary
Use the <file> element to find the existence of files with a specific name, for example, an ibm-webservices-ext.xmi file. For a better understanding of the <file> condition, see the JavaDoc for the File class.
Construct a <file> element
<file> element attributes
| Attribute name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
filename |
String |
Match the file names against the provided parameterized string. This attribute is required. |
as |
VARIABLE_NAME |
A variable name assigned to the rule so that it can be used as a reference in later processing. See the as="MyEjbRule" |
from |
VARIABLE_NAME |
Begin the search query with the filtered result from a previous search identified by its Example: from="MyEjbRule" |
<has-hint> syntax
Summary
Use the <has-hint> element to test whether a file or line has a hint already associated with it. It is primarily used to prevent firing if a hint already exists, or to implement rules for default execution when no other conditions apply. For a better understanding of the <has-hint> condition, see the JavaDoc for the HasHint class.
The following is an example of a rule that checks to see if a hint exists for an IBM JMS destination message, and if not, includes it.
<rule id="websphere-jms-eap7-03000">
<when>
<javaclass references="{package}.{prefix}{type}Message" />
</when>
<perform>
<iteration>
<when>
<not>
<has-hint />
</not>
</when>
<perform>
<hint title="IBM JMS destination message" effort="1" category-id="mandatory">
<message>
JMS `{package}.{prefix}{type}Message` messages represent the actual data passed through JMS destinations. This reference should be
replaced with the Java EE standard API `javax.jms.{type}Message`.
</message>
<link href="https://docs.oracle.com/javaee/7/tutorial/jms-concepts003.htm#sthref2271" title="Java EE 7 JMS Tutorial - Message API" />
<tag>jms</tag>
<tag>websphere</tag>
</hint>
</perform>
</iteration>
</perform>
<where param="type">
<matches pattern="(Text|Stream|Object|Map|Bytes)?" />
</where>
<where param="prefix">
<matches pattern="(JMS|MQe|MQ)" />
</where>
<where param="package">
<matches pattern="com.ibm(\..*)?\.jms" />
</where>
</rule>Construct a <has-hint>
The <has-hint> element is used to determine if a hint exists for a file or line. It does not have any child elements.
<has-hint> element attributes
| Attribute name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
message |
String |
An optional argument allowing you to match the hint against the provided message string. |
<has-classification> syntax
Summary
Use the <has-classification> element to test whether a file or line has a classification. It is primarily used to prevent firing if a classification already exists, or to implement rules for default execution when no other conditions apply. For a better understanding of the <has-classification> condition, see the JavaDoc for the HasClassification class.
Construct a <has-classification>
The has-classification element is used to determine if a specified classification exists. It does not have any child elements.
<has-classification> element attributes
| Attribute name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
title |
String |
An optional title to match the classification against. |
<graph-query> syntax
Summary
Use the <graph-query> element to search the generated graph for any elements. This element is primarily used to search for specific archives. For a better understanding of the <graph-query> condition, see the JavaDoc for the QueryHandler class.
The following is an example of a rule that tests to determine if any ehcache packages are found.
<rule id="embedded-cache-libraries-01000">
<when>
<graph-query discriminator="JarArchiveModel">
<property name="fileName" searchType="regex">.*ehcache.*\.jar$</property>
</graph-query>
</when>
<perform>
<classification title="Caching - Ehcache embedded library" category-id="cloud-mandatory" effort="5">
<description>
The application embeds an Ehcache library.
Cloud readiness issue as potential state information that is not persisted to a backing service.
</description>
</classification>
<technology-tag level="INFORMATIONAL">Ehcache (embedded)</technology-tag>
</perform>
</rule>Construct a <graph-query>
<graph-query> element attributes
| Attribute Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
discriminator |
MODEL_TYPE |
The type of model to use for searching. This can be any valid model; however, it is recommended to use the |
as |
VARIABLE_NAME |
A variable name assigned to the rule so that it can be used as a reference in later processing. See the |
from |
VARIABLE_NAME |
Begin the search query with the filtered result from a previous search identified by its |
<graph-query> properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
name |
String |
The name of the attribute to match against within the chosen model. When using any file-based models, it is recommended to match on |
type |
property-type |
Defines the expected type of property, either |
searchType |
property-search-type |
Defines how the condition is matched. If set to |
<dependency> syntax
Summary
Use the <dependency> element to search dependencies defined within the application’s POM file to determine whether they are supported by the target runtime.
The following is an example of a rule that checks for all artifacts belonging to the org.springframework.boot group that have a version up to, and including, 1.6.0.
<rule id="springboot-00001">
<!-- rule condition, when it could be fired -->
<when>
<dependency groupId="org.springframework.boot" artifactId="{*}" toVersion="1.6.0" />
</when>
<!-- rule operation, what to do if it is fired -->
<perform>
<hint title="Unsupported version of Spring Boot" effort="3" category-id="mandatory">
<message>Spring Boot has to be updated to Spring Boot 2.0 before being able to be migrated to a version supported by Red Hat Runtimes</message>
<link href="https://access.redhat.com/articles/3349341" title="RHOAR Spring Boot Supported Configurations" />
<link href="https://access.redhat.com/articles/3348731" title="RHOAR Component Details Overview" />
<link href="https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot/wiki/Spring-Boot-2.0-Migration-Guide" title="Spring Boot 2.0 Migration Guide" />
</hint>
</perform>
</rule>