Eclipse Plugin Guide
Making open source more inclusive
Red Hat is committed to replacing problematic language in our code, documentation, and web properties. We are beginning with these four terms: master, slave, blacklist, and whitelist. Because of the enormity of this endeavor, these changes will be implemented gradually over several upcoming releases. For more details, see our CTO Chris Wright’s message.
1. Introduction
1.1. About the MTR plugin for Eclipse
You can migrate and modernize applications by using the Migration Toolkit for Runtimes (MTR) plugin for Eclipse.
The MTR plugin analyzes your projects using customizable rulesets, marks issues in the source code, provides guidance to fix the issues, and offers automatic code replacement, if possible.
1.2. About the Migration Toolkit for Runtimes
What is the Migration Toolkit for Runtimes?
The Migration Toolkit for Runtimes (MTR) is an extensible and customizable rule-based tool that simplifies the migration and modernization of Java applications.
MTR examines application artifacts, including project source directories and application archives, and then produces an HTML report highlighting areas needing changes. MTR supports many migration paths, including the following examples:
-
Upgrading to the latest release of Red Hat JBoss Enterprise Application Platform
-
Migrating from Oracle WebLogic or IBM WebSphere Application Server to Red Hat JBoss Enterprise Application Platform
-
Containerizing applications and making them cloud-ready
-
Migrating from Java Spring Boot to Quarkus
-
Updating from Oracle JDK to OpenJDK
-
Upgrading from OpenJDK 8 to OpenJDK 11
-
Upgrading from OpenJDK 11 to OpenJDK 17
-
Upgrading from OpenJDK 17 to OpenJDK 21
-
Migrating EAP Java applications to Azure
-
Migrating Spring Boot Java applications to Azure
For more information about use cases and migration paths, see the MTR for developers web page.
How does the Migration Toolkit for Runtimes simplify migration?
The Migration Toolkit for Runtimes looks for common resources and known trouble spots when migrating applications. It provides a high-level view of the technologies used by the application.
MTR generates a detailed report evaluating a migration or modernization path. This report can help you to estimate the effort required for large-scale projects and to reduce the work involved.
How do I learn more?
See the Introduction to the Migration Toolkit for Runtimes to learn more about the features, supported configurations, system requirements, and available tools in the Migration Toolkit for Runtimes.
2. Installing and configuring the MTR plugin
You can install the MTR plugin and configure it to use the MTR CLI for analysis execution.
2.1. Installing in a connected environment
You need a connected environment to install the MTR plugin.
The MTR plugin has been tested with the Eclipse integrated development environment (IDE) for Java Enterprise Developers 2023-03.
The following are the prerequisites for the Migration Toolkit for Runtimes (MTR) installation:
-
Java Development Kit (JDK) is installed. MTR supports the following JDKs:
-
OpenJDK 11
-
OpenJDK 17
-
Oracle JDK 11
-
Oracle JDK 17
-
Eclipse Temurin™ JDK 11
-
Eclipse Temurin™ JDK 17
-
-
8 GB RAM
-
macOS installation: the value of
maxprocmust be2048or greater.
-
JBoss Tools, installed from the Eclipse Marketplace
ImportantYou must also add JBoss Tools dependencies that are required by Eclipse during the MTR plug-in installation process. For more information, see Adding JBoss Tools dependencies for the MTR plug-in.
-
Mylyn SDK and frameworks, installed with Eclipse
|
Note
|
Eclipse is pre-configured for Java 17, and the plugin operates directly with Java 17. You can also run the plugin with Java 11, which requires setting the JRE version to Java 11 when creating up a new Eclipse project or importing an existing one. See step 6 below. |
-
Launch Eclipse.
-
From the menu bar, select Help → Install New Software.
-
Next to the Work with field, click Add.
-
In the Name field, enter
MTR. -
In the Location field, enter
https://marketplace.eclipse.org/content/migration-toolkit-runtimes-mtrand click OK. -
Select the Java version to use.
-
If using Java 11, in the JRE list, select JavaSE 11.
-
If using Java 17, leave the JRE selection unchanged.
-
-
Select all the JBoss Tools - MTR check boxes and click Next.
-
Review the installation details and click Next.
-
Accept the terms of the license agreement and click Finish.
-
Restart Eclipse.
2.2. Configuring the MTR plugin to use the MTR CLI for analysis execution
You can configure the MTR plugin to use the MTR CLI for analysis execution.
-
You have downloaded the MTR CLI from the Developers Website or Customer Portal and installed it locally.
-
Click the Configure MTR icon to open the configuration settings.
-
Populate the CLI field with the path to the parent directory of the CLI.
-
Click Apply.
3. Accessing the MTR tools
You can access the MTR plugin tools in the MTR perspective.
-
You must restart the Eclipse IDE after installing the MTR plugin.
-
Click Window → Perspective → Open Perspective → Other.
-
Select MTR and click OK.
The following components are displayed:
-
Issue Explorer displays the migration issues identified by the MTR plugin.
-
MTR Server is a separate process that analyzes projects, flags migration issues, and generates reports.
You can start, stop, and view the status of the MTR server in the Issue Explorer.
-
Issue Details displays detailed information about a selected issue, including the hint, severity, and any additional resources.
-
MTR Report is an HTML report generated by the MTR plugin. From the report landing page you can navigate to detailed reports, such as Application Details, Issues, and Dependencies.
NoteThe report is not generated by default. You must select the Generate Report option in the run configuration.
-
4. Analyzing your projects with the MTR plugin
You can analyze your projects with the MTR plugin by creating a run configuration, running an analysis, and then reviewing and resolving migration issues detected by the MTR plugin.
4.1. Creating a run configuration
You can create a run configuration in the Issue Explorer. A run configuration specifies the project to analyze, migration path, and additional options.
You can create multiple run configurations. Each run configuration must have a unique name.
-
You must import your projects into the Eclipse IDE.
-
In the Issue Explorer, click the MTR icon (
 ) to create a run configuration.
) to create a run configuration. -
On the Input tab, complete the following fields:
-
Select a migration path.
-
Beside the Projects field, click Add and select one or more projects.
-
Beside the Packages field, click Add and select one or more the packages.
NoteSpecifying the packages for analysis reduces the run time. If you do not select any packages, all packages in the project are scanned.
-
-
On the Options tab, you can select Generate Report to generate an HTML report. The report is displayed in the Report tab and saved as a file.
Other options are displayed. See About MTR command-line arguments in the CLI Guide for details.
-
On the Rules tab, you can select custom rulesets that you have imported or created for the MTR plugin.
-
Click Run to start the analysis.
4.2. Analyzing projects
You can analyze your projects by running the MTR plugin with a saved run configuration.
-
In the MTR perspective, click the Run button (
 ) and select a run configuration.
) and select a run configuration.The MTR plugin analyzes your projects. The Issue Explorer displays migration issues that are detected with the ruleset.
-
When you have finished analyzing your projects, stop the MTR server in the Issue Explorer to conserve memory.
4.3. Reviewing issues
You can review issues identified by the MTR plugin.
-
Click Window → Show View → Issue Explorer.
-
Optional: Filter the issues by clicking the Options menu
 , selecting Group By and an option.
, selecting Group By and an option.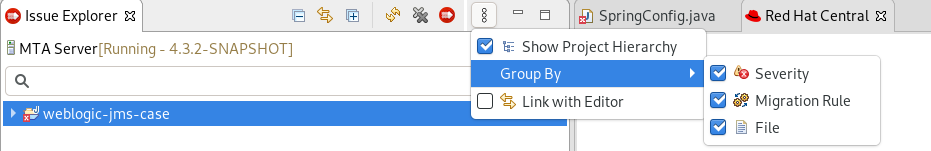
-
Right-click and select Issue Details to view information about the issue, including its severity and how to address it.
The following icons indicate the severity and state of an issue:
Table 1. Issue icons Icon Description 
The issue must be fixed for a successful migration.

The issue is optional to fix for migration.

The issue might need to be addressed during migration.

The issue was resolved.

The issue is stale. The code marked as an issue was modified since the last time that MTR identified it as an issue.

A quick fix is available for this issue, which is mandatory to fix for a successful migration.

A quick fix is available for this issue, which is optional to fix for migration.

A quick fix is available for this issue, which may potentially be an issue during migration.
-
Double-click an issue to open the associated line of code in an editor.
4.4. Resolving issues
You can resolve issues detected by the MTR plugin by performing one of the following actions:
-
You can double-click the issue to open it in an editor and edit the source code.
The issue displays a Stale icon (
 ) until the next time you run the MTR plugin.
) until the next time you run the MTR plugin. -
You can right-click the issue and select Mark as Fixed.
-
If the issue displays a Quick Fix icon (


 ), you can right-click the issue and select Preview Quick Fix and then Apply Quick Fix.
), you can right-click the issue and select Preview Quick Fix and then Apply Quick Fix.
5. Managing rules
The MTR plugin comes with a core set of System rules for analyzing projects and identifying migration and modernization issues.
You can create and import custom rulesets.
5.1. Viewing rules
You can view system and custom rules, if any, for the MTR plugin.
-
To view system rules, the MTR server must be running.
-
Click the Rulesets tab.
-
Expand System to view system rulesets or Custom to view custom rulesets.
-
Expand a ruleset.
-
Double-click a rule to open it in a viewer.
-
Click the Source tab to view the XML source of the rule.
5.2. Creating a custom ruleset
You can create a custom ruleset in the MTR perspective.
See the Rules Development Guide to learn more about creating custom XML rules.
-
Click the Rulesets tab.
-
Click the Create Ruleset icon (
 ).
). -
Select a project and a directory for the ruleset.
-
Enter the file name.
NoteThe file must have the extension
.windup.xml. -
Enter a ruleset ID, for example,
my-ruleset-id. -
Optional: Select Generate quickstart template to add basic rule templates to the file.
-
Click Finish.
-
The ruleset file opens in an editor and you can add and edit rules in the file.
-
Click the Source tab to edit the XML source of the ruleset file.
You can select the new ruleset when you create a run configuration.
5.3. Importing a custom ruleset
You can import a custom ruleset into the MTR plugin to analyze your projects.
-
Custom ruleset file with a
.windup.xmlextension.See the Rules Development Guide for information about creating rulesets.
-
Click the Rulesets tab.
-
Click the Import Ruleset icon (
 ).
). -
Browse to and select the XML rule file to import.
The custom ruleset is displayed when you expand Custom on the Rulesets tab.
5.4. Submitting a custom ruleset
You can submit your custom ruleset for inclusion in the official MTR rule repository. This allows your custom rules to be reviewed and included in subsequent releases of MTR.
-
Click the Rulesets tab.
-
Click the Arrow icon (
 ) and select Submit Ruleset.
) and select Submit Ruleset. -
Complete the following fields:
-
Summary: Describe the purpose of the rule. This becomes the title of the submission.
-
Code Sample: Enter an example of the source code that the rule should run against.
-
Description: Enter a brief description of the rule.
-
-
Click Choose Files and select the ruleset file.
-
Click Submit.